Today, all the Organisations are moving to Spring boot which is obvious and a smarter way to increase the productivity and features provided. And if you are preparing for your next JAVA Interview then don’t be surprised hearing Spring boot questions. Spring boot questions are the most asked questions in the advanced java interview and you should be ready to tackle those questions to get a better offer in your hand.
We will be providing some advance spring-boot interview questions which should be prepared for an interview related to microservices, rest APIs and of course Spring framework. Our recommendation will be to be an expert in these questions and related topics.
What is Spring boot?
Spring Boot is an opinionated library that allows creating executable Spring applications with a convention over configuration approach. It requires a minimum configuration to create production-ready applications. Let’s look at some most advanced interview questions related to Spring boot below.
1. How Can we reflect on the changes without restarting the server?
With the Devtools dependency, we can achieve this feature. The Devtools module helps to auto-deploy the changes to the application which improves the productivity of a programmer and also the manual efforts can be eliminated. This module should be disabled in the production environment.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
2. What is ELK Stack and why do we use this?
ELK is in high demand in the spring-boot applications due to its high-level logging systems. ELK stack is basically the collection of three different open-source product which is ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kabana.
ElasticSearch – It works as a search engine that works as a NoSQL database and searches and analyzes the large collection of data.
Logstash – Logstash is simply a log pipeline tool that accepts the data and executes it into different parts and exports it into different target locations.
Kabana – It works as a UI layer above the ElasticSearch.
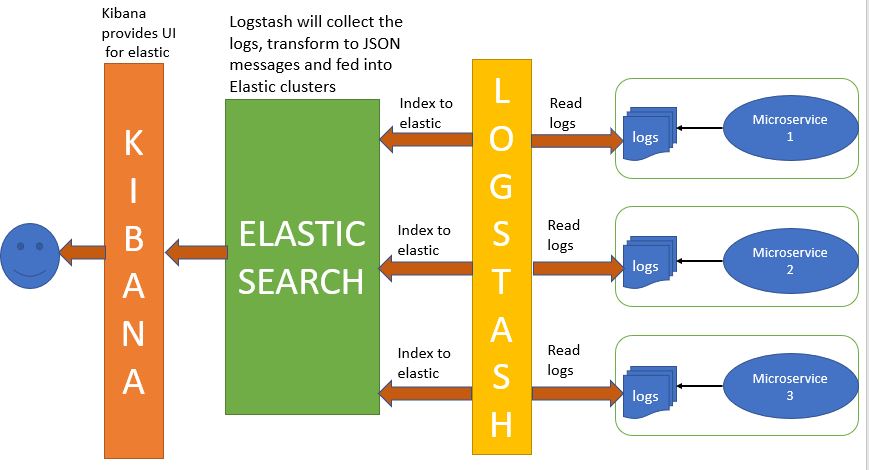
Usage of ELK : For the practical example, Suppose there are 100 number of application running which are generating the logs on the same target location, and if we need a single log file of the particular application then that will be a tedious task to do, With the ELK we can search the particular log file in the real-time without any inconvenience.
3. How will you monitor the health of Spring Boot microservices?
We can monitor each service with the help of the Spring Actuator. The actuator shows the status of the individual microservice if it is up or down, along with the status of the components like database and other integrations as well. The only and the most annoying drawback is that we need to check each endpoint of the services to know the health, and this can also be solved by spring boot admin client modules.
4. Spring Boot is known for AutoConfiguration, how this Autoconfiguration works actually?
Springboot autoconfiguration is implemented in spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar with many classes like AopAutoConfiguration, JacksonAutoConfiguration, SecurityAutoconfiguration, DataSourceAutoConfiguration and many more. These classes consist of the logic when and how the autoconfiguration will be implemented. For instance, if Hibernate jar is available in the classpath then Datasource bean will be auto-configured with the help of the DataSourceAutoConfiguration class. We can also have our own AutoConfiguration Class with the help of @conditional.
5. How to write a custom auto-configuration class?
We can write our own logic of autoconfiguration in the custom class, For this, we need to extend the SpringBootConditionclass and use it with the @Conditional annotation. Once the logic is ready we need to register this class as an autoconfiguration. This is done by making an entry of the full class name in META-INF/spring.factories like below.
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
\com.empathybroker.samples.autoconfigure.SampleAutoConfiguration6. What are ControllerAdvice and ExceptionHandler, state the difference?
ControllerAdvice and ExceptionHandler are used by spring boot in exception handling. Both of the annotations are used to handle the exceptions in an API and send the response to the client in case of any incident happens.@ControllerAdvice handles the Global errors which means any exception occurred over the application will be handled by this annotation. The class denoted by @ControllerAdvice annotation would be responsible to handle the exceptions occurred in any controller within the application.@ExceptionHandler is used to handle the exception specific to the controller. If someone wants to handle the special event within a controller which also sends a custom response to the client then this annotation can be implemented within the controller. This annotation handles the exception locally within a controller and can’t be accessed outside the controller.
7. What is Spring CLI, how this is beneficial to Programmers?
The Command Line Interface of Spring-boot to run the Groovy scripts is a very helpful and fast execution system, which is only supported by java 1.8 or above. To run the groovy file, for Instance, Hello.groovy in spring CLI the command will be – spring run HelloWorld.groovy .
To set up the Spring CLI, We need to download the springcli package from the official spring website and set the path in Environment Variables.
Groovy files help the programmers to reduce the boiler-plate code and improve the quality of the application.
8. What is Swagger, how swagger boost the efficiency of Springboot?
Swagger provides a UI to access the REST API through the Browsers. This is available to use as an open-source project and completes the need for documenting the REST APIs. For Instance, if we need to maintain a document for the Rest API manually, There are some chances that it will soon get outdated. Here Swagger provides the dynamic and automated way to document each and every API endpoints with the help of HTML, JS, and CSS.
Springboot helped us to create restApi very easily, and interaction with these APIs is an important task. Swagger provides the interaction with the RESTAPI with the help of the UI framework which easily describes how the API is responding to different parameters. In the client-server architectures Swagger Help to maintain the synchronization of the API documentation at the same speed.
9. Explain default Embedded Server in Spring-boot? Explain the benefit of the same?
Whenever we create an application that is deployable. For this, Application servers like Tomcat, JBoss was required. Springboot came up with a feature of an embedded server which is Tomcat. So in spring boot, the application runs just like a normal java application with the help of an embedded tomcat server. Embedded server means our application is having the binaries of the server (tomcat.jar).
When we include spring-boot-starter-web dependency on the spring boot project. This dependency also includes the starter tomcat dependency which can also be changed to other servers by removing the tomcat dependency and providing the dependency of other servers like spring-boot-starter-jetty or spring-boot-starter-undertow.
10. What is the default port of Embedded Tomcat in Springboot, how can we change it?
In spring-boot by default, Port:8080 is used by Tomcat which can be changed by adding the property server.port :PORT in application.properties file.
11. What are the log levels in Springboot?
There are multiple logging levels available in spring-boot for different loggers. Such as TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, OFF . By default Spring-boot uses INFO logging level which can be changed through the application.yml or application.properties file like below:
logging:
level:
root: ERROR
org.springframework.web: ERROR
com.jstobigdata: DEBUG
org.hibernate: ERROR
12. What are profiles in the spring-boot?
Spring-boot comes with the ultimate features Profiles, This helps our application to behave differently in different environments. This can be achieved by @Profile which resides under `spring-context.jar`
@Profile registers the bean as per the conditions provided in the configuration files. For Instance, Enable the DEBUG level logs in the DEV profile and ERROR level logs in the live environment.
13. Can we run the spring-boot application through the command line?
Yes, we can run our spring-boot app on the command line by using java- jar or any builder (Example- Maven). With java -jar myApplication.jar and with Maven mvn spring-boot:run.
14. What are the differences between .yml and .properties config file, which one we should use in spring-boot?
| .YML | .PROPERTIES |
| It contains Hierarchical Structure. | It has Non-Hierarchical Structure. |
| If you are using spring profiles, you can have multiple profiles in one single .yml file. | Each profile need one separate .properties file. |
| Human Readability is comparitively good. | Human Readability is not enough as compared with .yml files. |
| Getting used by many new languages like – Java , Ruby, Python. | Only Supported by Java. |
| Tyep Saferty (While fetching value, we get the value with the same type as defined in the file . We get int, string as defined in the yml file). | We get only string while fetching the value from properties file whether the declaration is any of the type. |
As per the differences .yml file is considered to use over the .properties because of the features like type safety, .yml provides better supports in case of multiple applications are using the same .yml files, and it is also supported by different languages.
15. How do we generate an executable JAR from Spring-boot?
Sping-boot can produce an executable jar that can be executed or deployed at any platform. To generate this we need to follow the below steps:
- Change the
<packaging>jar<packaging>inpom.xml - We need to add the dependency of
spring-boot-maven-plugininpom.xmllike below - Run the command
mvn clean packagewhich will generate the executable jar in the `targetfolder.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
Please share your feedback about this article in the comments below. Do share your favorite question below, if it is not included in the list.
